HTML Tutorial
Menu
HTML Forms
Menu
HTML Graphics
Menu
HTML Media
Menu
HTML API
Menu
Html Introduction
HTML is defined as the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
What is an HTML?
- HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
- HTML defines the structure of a Web page.
- HTML consists of a series of elements.
- HTML elements indicate the browser’s how to display the content.
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as “this is a heading”, “this is a paragraph”, “this is a link”, etc.
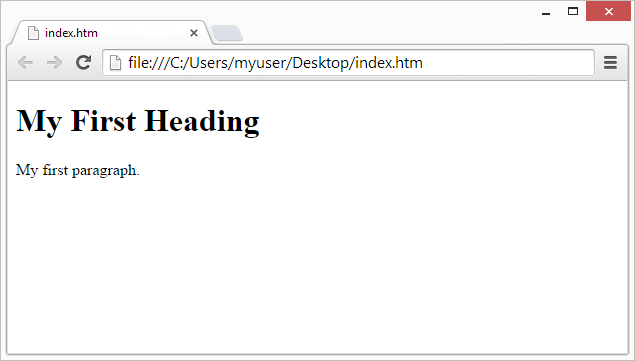
A Simple HTML Document
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
- The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration describes that this document is an HTML5 document.
- The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page.
- The <head> element consists of meta information about the HTML page.
- The <title> element mentions the title for the HTML page.
- The <body> element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the contents that is visible, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
- The <h1> element defines a large heading.
- The <p> element defines a paragraph.
What is mean by HTML Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
<tagname> Content goes here… </tagname>
The HTML element includes everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
Like:
Start tag </h1> Element content </h1> End tag
Web Browsers
All the HTML documents are displayed in the web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) whose purpose is to display the HTML contents correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags directly, instead uses them to understand how to display the document: